Laser Photocoagulation
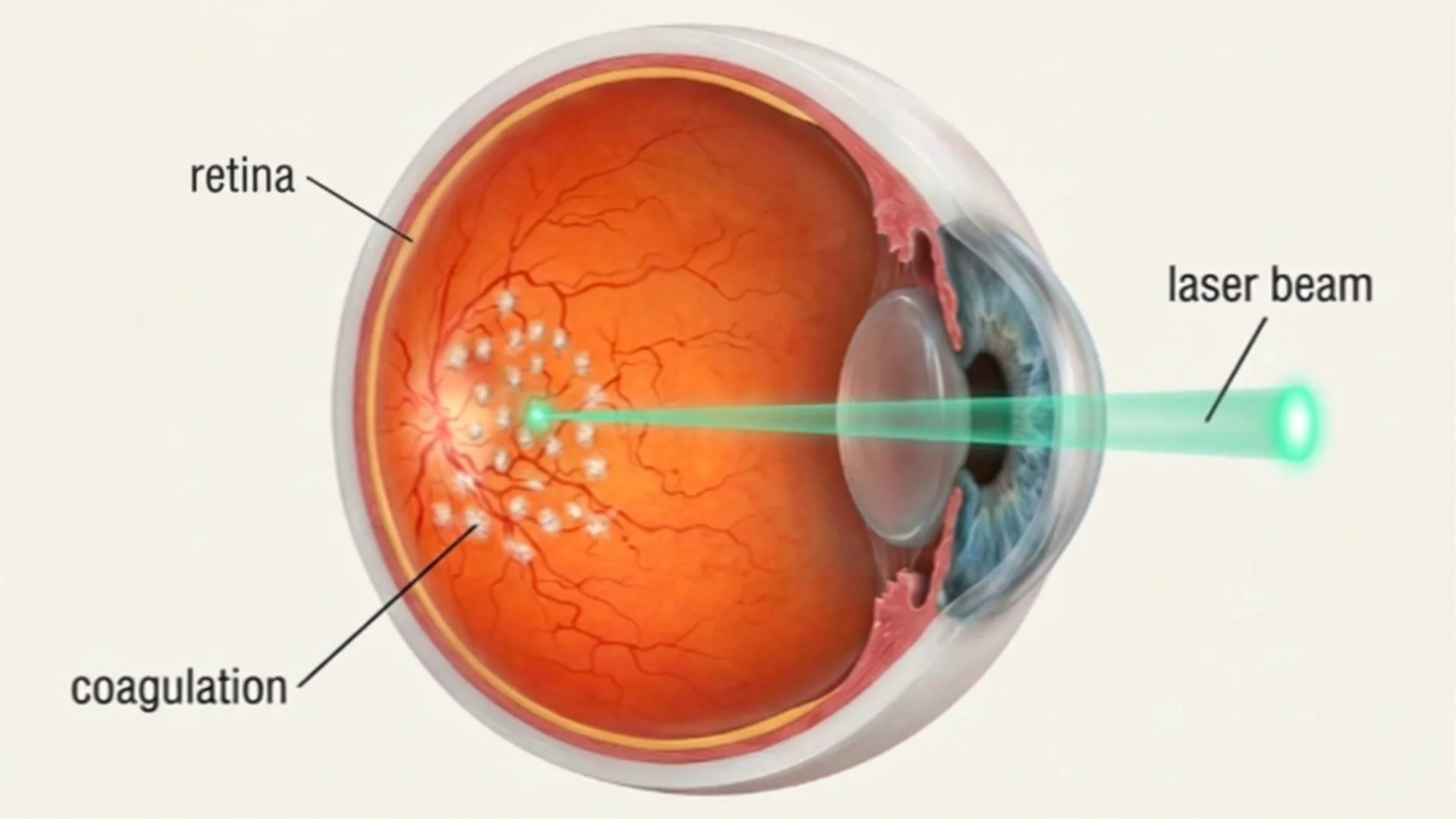
Laser photocoagulation is a treatment that uses focused light energy to seal or destroy abnormal blood vessels in the retina. This procedure plays an important role in managing several sight-threatening conditions, particularly those related to diabetes and retinal tears.
How It Works
During laser photocoagulation, a specially calibrated laser beam creates controlled, tiny burns on the retina. These burns serve different purposes depending on the condition being treated:
For diabetic retinopathy, the laser reduces the oxygen demand of damaged retinal tissue, which helps decrease the signals that promote abnormal blood vessel growth. The National Eye Institute notes that this treatment has been used effectively for decades to preserve vision in patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy.
For retinal tears, the laser creates a barrier of scar tissue around the tear, preventing fluid from passing beneath the retina and causing detachment.
Conditions Treated
Laser photocoagulation may be recommended for:
Proliferative diabetic retinopathy where abnormal blood vessels threaten vision
Diabetic macular oedema in certain cases
Retinal tears or holes at risk of progressing to detachment
Retinal vein occlusion complicated by abnormal vessel growth
Certain retinal vascular conditions requiring vessel closure
The Procedure
Laser photocoagulation is performed as an outpatient procedure:
Anaesthetic drops numb the eye
A special contact lens is placed on the eye to focus the laser
The ophthalmologist delivers precise laser applications to targeted areas
Duration varies from 10-15 minutes for focal treatment to 30-45 minutes for panretinal photocoagulation
Multiple sessions may be required depending on the condition
Research from landmark clinical trials, including the Diabetic Retinopathy Study and Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study, established this treatment as effective in reducing the risk of severe vision loss in appropriate candidates.
What to Expect
During treatment, you may see bright flashes of light and feel mild discomfort. Some patients describe a sensation similar to a rubber band snapping against the skin. More extensive treatments may cause temporary aching.
Immediately after the procedure, your vision will be blurry from the dilating drops and the bright laser light. This typically resolves within several hours, though some temporary visual changes may persist longer.
Potential Risks
While laser photocoagulation can preserve central vision, patients should understand the following:
Peripheral vision reduction is expected with panretinal photocoagulation, as this is how the treatment works
Night vision and dark adaptation may be affected
Temporary increase in macular swelling may occur initially
Mild discomfort during and after the procedure
Rare but serious risks include inadvertent damage to central vision, bleeding, or vision loss
The decision to proceed with laser treatment involves weighing these effects against the risk of vision loss from the underlying condition if left untreated.
Recovery and Outcomes
Most patients can resume normal activities the same day or the following day. Driving should be avoided until vision has cleared from the dilating drops.
For retinal tears, the laser-induced adhesion typically reaches full strength within two weeks. Close monitoring during this period is important.
For diabetic retinopathy, the treatment aims to stabilise the condition and prevent further deterioration rather than restore lost vision. Ongoing monitoring and possible additional treatment sessions are typically required. Continued management of diabetes and blood pressure remains essential.
Medical Disclaimer: This information provides general guidance about laser photocoagulation and should not replace professional medical advice. Treatment outcomes depend on the underlying condition and individual factors. The procedure aims to preserve vision and prevent further deterioration rather than restore vision already lost. Please consult with our ophthalmologists for assessment and recommendations specific to your situation.
Seek immediate attention if you experience: New flashes of light, sudden increase in floaters, shadow or curtain across your vision, or severe pain.

