
Dr Ajeet Madhav Wagle
MBBS(India) FRCS(Edinburgh) FAMS(Ophthalmology)(Singapore)
By Dr Ajeet Madhav Wagle, Medical Director and Senior Consultant Ophthalmologist, International Eye Cataract Retina Centre at Mount Elizabeth Medical Centre and Farrer Park Medical Centre, Singapore
Each month, the American Academy of Ophthalmology recognises one or more observances dedicated to raising awareness about eye health topics. This October, we want to raise awareness of the potential complications of contact lens wear, especially the harmful effects associated with self-prescribed cosmetic contact lenses.
Appropriately prescribed contact lenses by eye care professionals are generally considered relatively safe. However, self-prescribed use of cosmetic contact lenses may come with significantly higher risks.
It is important for contact lens wearers to be aware of the potential complications associated with contact lens use. In fact, some contact lens complications can cause permanent visual impairment and even blindness.
Contact lenses can improve quality of life by not only correcting the optical errors of the eye but also by providing a better appearance and lesser restriction of activities. Contact lenses can be used to treat corneal injuries as well as to control myopia (or short-sightedness). Contact lenses may be soft lenses (made of hydrogel or silicone hydrogel materials) or rigid gas permeable (RGP) lenses. Soft lenses are available as daily disposable lenses, fortnightly disposable lenses or monthly disposable lenses.
Some symptoms of concern with contact lens use are significant dryness, eye pain, redness, blurred vision, increased sensitivity to bright lights and presence of a “white spot” on the cornea. Here are some potential health issues all contact lens wearers should be aware of:
DRY EYES
Dry eye is the most common eye problem associated with contact lens wear. As many as half of all contact lens users have symptoms of dry eye such as eye redness, tearing, foreign body sensation and a tired feeling in the eyes.
Dry eye can result from reduced tear fluid quantity, increased evaporation of tear fluid, poor quality of tear fluid or a combination of these factors. A detailed eye evaluation is recommended to understand the underlying cause of the dry eye so that treatment can be customised for individual patients. In general, preservative-free artificial tear substitutes, anti-inflammatory medications and lacrimal punctal plugs are often prescribed to treat dry eye associated with contact lens wear.
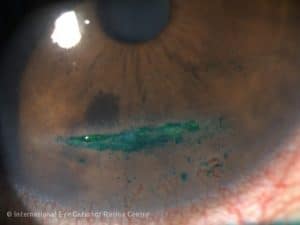
CORNEAL PROBLEMS
Corneal surface erosions or abrasions are common and may occur during insertion or removal of an over worn, poorly fitting or improperly cleaned contact lens. Significant pain, increased sensitivity to bright lights and tearing are prominent symptoms. Corneal surface problems are treated with lubricant, antibiotic and eye muscle relaxing eye drops.
Swelling of the cornea, distortion of the cornea, new blood vessel growth into the clear cornea and reduced corneal sensations are some of the effects of long-term use of extended wear contact lenses. The use of contact lens materials with a higher oxygen permeability and modification to the contact lens wearing schedule can usually help the condition. Switching from a soft contact lens to a RGP lens may also be recommended.
CONTACT LENS FIT PROBLEMS
Inappropriate fitting of the contact lens over the cornea can either result in a tight lens syndrome or easy displacement of the contact lens over the cornea. A systematic and customised contact lens fitting by eye care professionals can reduce such problems.
CORNEAL INFLAMMATION
Eye itch, redness, tearing and discomfort can occur because of giant papillary conjunctivitis. These symptoms are more common in individuals with a previous history of allergies and in those using silicone hydrogel soft contact lenses. Anti-inflammatory, anti-allergy and lubricating eyedrops are often prescribed to treat the condition. If the condition is severe, discontinuation of contact lens use may be recommended.
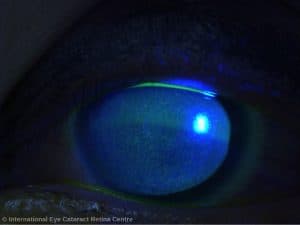
CORNEAL INFECTION
The most serious of all contact lens complications is corneal infection or corneal ulcer. It is a serious sight-threatening complication and can lead to permanent blindness and corneal scarring.
Corneal infection may be caused by a variety of microorganisms (e.g. bacteria, viruses, fungi and protozoa). Poor contact lens hygiene, contamination of contact lens solution, extended wear, poor corneal oxygen concentration and corneal injury during insertion or removal of contact lens are major risk factors. Use of self-prescribed cosmetic contact lenses significantly increases the risk of infection as these lenses may not always be sterile and are often procured from unreliable sources.
Common symptoms of corneal infection are severe eye pain, redness, increased sensitivity to bright lights, tearing and blurred vision. A white spot may also be noticed on the cornea.
For optimal management, corneal samples are usually collected from the affected eye and sent along with the contact lens and/or contact lens casing for microbiological testing. Treatment often involves the use of intensive broad-spectrum antibiotic eye drops round the clock along with very close monitoring of the eye condition. The treatment plan may be modified based on the test results. Contact lens wear is temporarily ceased. In cases which respond poorly to medical treatment, corneal surgery is occasionally required.
In summary, contact lens-related problems can vary from mild to very severe sight-threatening complications with long-term sequelae. If you are a contact lens user, seek immediate medical advice for any symptom of pain, redness, blurred vision or a white spot on the cornea. Prompt treatment can help save sight. Avoiding the use of self-prescribed cosmetic contact lenses can reduce your risk of serious eye problems.

